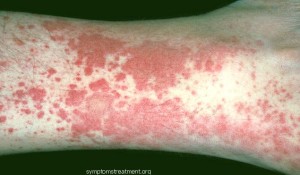
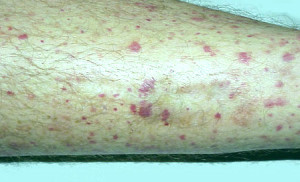
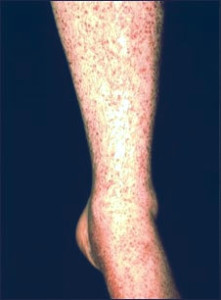
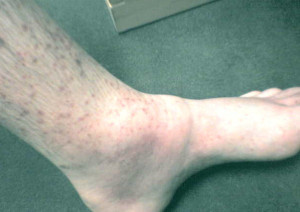
What is Vasculitis ?
Vasculitis is a disorder that results in inflammation of the blood vessels. The condition leads to several changes in the blood vessels walls such as weakening, scarring, thickening and narrowing.
There are various forms of vasculitis. Some types are chronic and last for an extended period while other forms are acute and may last for a very short duration. Cases of vasculitis can be very severe as the affected blood vessels tend to carry decreased supply of blood to various organs and tissues. This can result in organ and tissue damage as well as fatality.
Anyone can be affected by vasculitis, though individuals belonging to a certain group may be more vulnerable to the condition. Some types of vasculitis tend to improve by themselves whereas other forms may require medications over a long period of time.
Vasculitis is often referred to by other names such as arteritis or angiitis.
Symptoms of vasculitis
The symptoms of vasculitis vary as per the blood vessel and the organ that is affected. Some of the general signs of the condition are listed below:
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Loss of weight
- Excessive tiredness or fatigue
- Joint and muscle pain
- Nerve abnormalities such as weakness or numbness
The symptoms of various forms of vasculitis are discussed below:
- Buerger’s disease: It causes clots and inflammation of the blood vessels present in the extremities. It has a strong association with cigarette smoking and tends to cause pain in the upper and lower limbs, and ulcers on toes and fingers.
- Behcet’s syndrome: It results in inflammation of the veins and arteries and appears in the twenties or thirties. Symptoms include eye inflammation, genital and oral ulcers and acne-like skin lesions.
- Churg-Strauss syndrome: Often associated with asthma, the condition affects the lung blood vessels.
- Giant cell arteritis: It generally affects the elderly and causes inflammation of the head arteries, particularly the temples. Symptoms include pain in jaw while chewing, headaches, double or blurred vision or even blindness and scalp tenderness. Giant cell arteritis is often associated with another condition called PMR which causes inflammation and pain in the large joints. PMR results in muscle stiffness or pain in the thighs, hips, upper arms, shoulders and neck.
- Cryoglobulinemia: It shows symptoms such as nerve damage, purpura rash on the lower extremities, weakness and arthritis. The condition is mostly associated with infections by hepatitis C.
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura: It causes inflammation of the blood vessels in the bowels, skin, kidneys and joints. Symptoms include bloody urine, purpura rash on legs, buttocks and feet, joint and abdominal pain.
- Kawasaki disease: It often affects children below 5 years and shows symptoms such as skin rash, fever and eye inflammation
- Hypersensitivity vasculitis: The condition may be triggered by an allergy to an infection or a drug and leads to the formation of red spots on the skin
- Microscopic polyangiitis: It affects the smaller blood vessels in the lungs, kidneys and skin and shows symptoms such as nerve damage, inflammation of smaller blood vessels in the kidneys, fever, skin lesions and weight loss.
- Takayasu’s arteritis: It typically affects young women and occurs in the largest arteries such as the aorta. Symptoms include visual abnormalities, headaches, diminished or absent pulses, sensation of cold or numbness in the extremities and hypertension.
- Polyarteritis nodosa: It affects blood vessels that are midsized in various regions of the body such as kidneys, skin, peripheral nerves, heart, intestines and muscles. Symptoms include kidney abnormalities, joint and muscle pain, skin ulcers, abdominal pain and purpura rash.
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis [Wegener’s]: It results in inflammation of the blood vessels in the sinuses, lungs, throat, kidneys and the nose. Signs include chronic sinus infections, nasal stuffiness, kidney damage and nosebleeds.
Causes of vasculitis
Vasculitis is caused due to the mistaken recognition of the blood vessel cells as invaders of the body by the immune system. The immune system then attacks the blood vessels resulting in the condition. The exact reasons for this action of the immune system are unknown, but studies suggest that it may be triggered by certain cancers, an allergic reaction or an infection or due to the presence of some immune system abnormalities.
- Vasculitis results in inflammation of the blood vessels which cause them to become thicker and then narrower. This leads to decreased supply of blood, oxygen and essential nutrients to the various affected organs. Sometimes, the blood flow may be obstructed due to the development of a blood clot, whereas at other times vasculitis may result in weakening of the blood vessels causing fatal aneurysm.
- There are two types of vasculitis based on the causes. Primary vasculitis has no known cause.
- Secondary vasculitis develops due to the presence of another disease, which may be caused due to immune system diseases, blood cell cancers, allergic reactions and infections.
Treatment of vasculitis
Treatment of vasculitis is specific to the type of vasculitis that affects the patient. Some of the treatment methods are as follows:
- Steroid medications such as corticosteroids may be given to control inflammation.
- Severe cases of vasculitis may require immunosuppressant drugs to inhibit the activities of the immune system
- The above medications have many side effects and hence should be consumed only after consultation with a physician.
Vasculitis pictures