What is tinea versicolor ?
It is a common fungal infection of skin and is experienced by most adults. It is a harmless condition caused by the yeast, known as Malassezia furfur which is known to live on the skin of most individuals without causing any serious health issues. Tinea versicolor is often referred to by the name pityriasis versicolor.
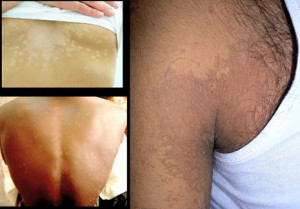
Tinea versicolor causes the discolored, thin scaly patches over the skin, which can be identified through a microscope. This fungal infection is not a contagious one. The result and the effect of the fungus infection is that the normal condition of the skin pigmentation gets corrupted.
The condition of infection is triggered by changes in the immune system, or the hormonal changes and high levels of atmospheric humidity. It is common among teenagers and in adults. The persons affected by this infection normally do not experience any medical complications.
The effect of tinea versicolor is that it changes the color of the skin, either lighter or darker than the normal surrounding color, and is clearly visible during sun exposure.
Medications can cure infection, but there is no guarantee to stop its recurrence. Medicines such as antifungal lotions, creams, shampoos cure infections. Even after the treatment, skin color may remain unchanged for several weeks, till the skin gets re-pigmentation. One has to maintain high level of hygiene in warm climates to avoid the condition.
Symptoms of Tinea versicolor
The signs and symptoms of tinea versicolor are discussed below:
- Skin patches develop and vanish after treatment. The chemicals produced by the fungus, changes the color of the skin lighter, by inhibiting the production of skin pigments.
- Though the change of color to normal takes place after treatment, it may take several months for that change to occur.
- It does not leave a lasting scar or color changes on the skin.
- Skin infection has the appearance of a thin tissue coat.
- May have mild itching
- Color patches grow very slowly and are clearly visible during exposure to the sun.
- The tinea versicolor causing fungus attacks irrespective of the race and the type of skin color that one has.
- The signs of the condition are more clearly visible on dark skin.
- Skin patches can be of any color, viz. white, brown, pink, dark and tan.
- Infection is more common in humid and warm climates. Normally the body area affected are, neck, back, upper arms, chest and folds.
Diagnosis of Tinea versicolor
Take a small scrap of the affected skin, put a drop of potassium hydroxide on it, and examine it under a microscope. The presence of the yeast which has caused the tinea versicolor can be confirmed by this simple procedure.
One need to consult a doctor, if:
- When self care treatment fails to provide the solution
- If the fungus infection recurs
- When the patches cover a large portion of the skin on the body
Causes of Tinea versicolor
Convenient place for the growth of fungus on skin is the hair follicles that open onto the skin surface. The fungus can attack even healthy skin and cause the disorder. Tinea versicolor and the appearance of the characteristic discolored patches on the skin tends to occur when the yeast become overgrown.
The following factors can induce the growth of the fungus:
- Oily skin
- Hormonal changes
- Changes in immune system, which decrease the capacity of the immune system to fight such fungus attacks
- Excessive perspiration
- Warm and humid climate
Tinea versicolor treatment
Generally the medicines available over the counter are applied over the affected portion. If there is no response to such traditional medicines, then one may approach the doctor to avail of stronger medications. The doctor may prescribe the following medicines for treating tinea versicolor:
Topical medicines:
- Ketoconazole
- Ciclopirox
- Selenium sulfide 2.5% lotion
Oral medications:
- Ketoconazole
- Itraconazole
- Fluconazole
Even after the successful treatment, it may take few months for changing the skin color to normal. Moreover it may recur if the climate is humid and warm. If the disease is persistent, one may need to take the medication every two months to avoid any recurrence.
In case of mild infections, the medicines, such as antifungal cream, ointment, shampoo or lotion available over the counter is enough to tackle disease. Most of the fungal infections are well controlled by the topical medicines such as:
- Terbinafine
- Selenium sulfide shampoo
- Miconazole Clotrimazole
One may need to apply the topical agent twice a day after cleaning the affected skin, for a period of two weeks. If the topical agent was used in a shampoo form, then it should be rinsed off after 10 minutes. If there is no response or relief from these medications, even after four weeks, then he/she should contact the doctor for stronger medicines.
Wearing synthetic and tight clothing should be avoided. Also applying oil on skin should be avoided.
For preventing the recurrence of infection, doctor may prescribe certain medicines which have to be taken once or twice in a month. Following are some of the preventive medicines that a doctor may prescribe:
- Itraconazole
- Ketoconazole
- Selenium sulfide lotion for applying on the infected portion, every two to three weeks
Tinea versicolor pictures
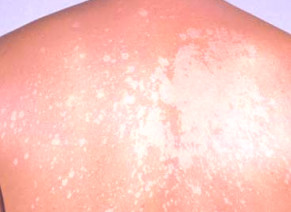
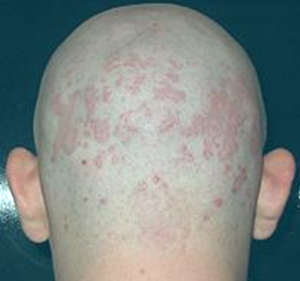
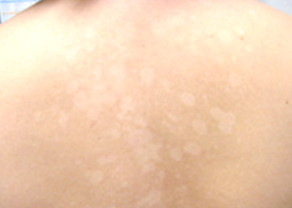
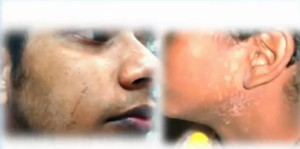
Awesome issues here. I am very happy to peer your article. Thank you so much and I’m having a look forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?