Ear infections in adults are of two types, outer or external ear infections and acute or middle ear infections.
When the outer ear is infected with germs and other bacteria, then it results in otitis externa or outer ear infection.
When the inner or the middle ear comprising of the ear canal and other parts of the middle ear are infected with germs, viruses and bacteria, then it results in otitis media or middle ear infection.
Ear Infection Symptoms in adults
The signs and symptoms of ear infection in adults are mentioned below:
Outer ear infections in adults-
- • The insides of the ear may have increased irritation and itching
- There may pus-like discharge from the ears
- The skin on the ears may become increasing dry and scaly and result in flaking
- Increased redness or flushing of the ears
- Increased instances of fever and increased body temperature
- Increased sensations of pain when one touches an infected ear, or whist moving one’s head.
Middle ear infection symptoms in adults
- Ear pain
- Impaired or decreased hearing capabilities
- Watery or fluid discharge from the ear
- Soreness of the throat
- Sensations of pressure or fullness in the ear
- Increased irritability
- Increased ear pain when one is lying down
- Sleep disturbances or problems
- Fidgety or irritating ear
- Diarrhea
- A loss in the sense of balance
- Decreased appetite
- Increased instances of fever accompanied by headaches
- Vomiting
- Untreated ear infections as children, may result in delays in development of speech and other factors, that may lead to an impaired adulthood
- The ear infection may spread to other tissues, like the brain, etc causing serious complications
Causes of ear infection in adults
Ear infections are usually caused by the collection of bacteria, viruses and other germs in the outer and middle ear. In addition, other illnesses such as allergies, flu or cold that cause inflammation and blockage of the throat, ear canal and the nasal passage may also result in infection of the ear or its tissues.
The causes and risk factors of ear infection are listed below:
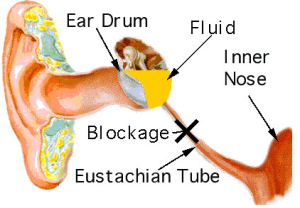
- • The ear canal or the Eustachian tubes maintain the air pressure in the ear, remove the discharge from the middle ear and refresh the air in the ear. Illnesses such as cold, allergies, etc cause the congestion of these tubes resulting in deposition of excess fluids in the middle ear. Infection of these fluids by bacteria and viruses result in ear infection and pain
- Swelling or inflammation of the adenoids may also result in congestion of the Eustachian tubes leading to ear infection and pain
- Changing weather conditions and climate may bring the onset of flu, cold and other illnesses increasing the risk to ear infection in adults
- A strong family history of ear infections and seasonal allergies increases the risk to ear infections
- Constant exposure to polluted air or tobacco smoke may also increase the vulnerability to ear infection in adults
Treatment of ear infection in adults
Some of the methods to treat ear infection and its symptoms in adults are as follows:
- One may alleviate ear pain by using a warm compress
- Pain medications or pain killers and eardrops may also assist in treating pain and infection
- Bacterial infections of the ear can be treated with antibiotics
- In case of serious ear infections in adults, an ENT specialist must be consulted.