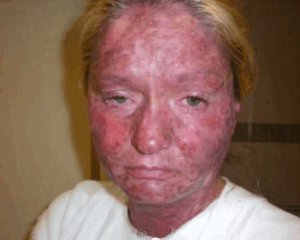
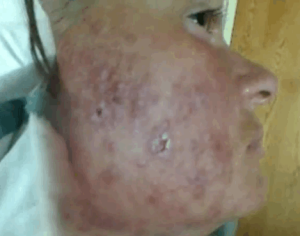
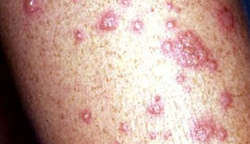
What is Stevens Johnson Syndrome?
Stevens Johnson syndrome or SJS is a type of skin disease that occurs due to drug reaction. It is a serious skin problem that mainly affects the mucous membranes and the skin. People with SJS exhibit flu-like symptoms and experience intense pain. The disease causes skin rashes and blistering, making the skin’s top layer to shed off.
Stevens Johnson syndrome requires immediate treatment to prevent it from aggravating. The treatment is aimed at curing the underlying cause, managing the symptoms and reducing the probability of complications. Still, recovery period may run from several weeks to a few months. There is nothing that can be done to keep it from happening, so familiarizing the symptoms is important to allow for its early detection and reduce the severity of the disease.
Stevens Johnson syndrome symptoms
A person that is affected by the syndrome will experience coughs, sore throat, fever and burning sensation in the eyes. The individual may not know that he or she has Stevens Johnson syndrome until skin rashes emerge several days after the early symptoms appear. Among the manifestations of the syndrome include:
- Skin pain
- Inflamed tongue and face
- Hives
- Skin sloughing
- Purple or red rashes on the skin
- Blisters on the skin, mouth, eyes, nose and mucous membranes
Incidence of Stevens Johnson syndrome
The disease is categorized among the rare diseases, which means it happens in less than 200,000 Americans. Anyone can be affected by the disorder, though statistics have shown that older people are at higher risk due to the purposeful use of drugs that could cause SJS. Those who have compromised immune systems, such as AIDS patients, are also at risk. In addition, genetics may also play a role in the development of the syndrome by means of the HLA-B12 gene. Whether or not a person has the risk factors, it is important to be aware of the symptoms and seek prompt medical attention when the signs appear.
Cause of Stevens Johnson Syndrome
It is not clear why SJS occurs but it tends to arise as a result of an allergic reaction to certain drugs, such as:
- Penicillin
- Anticonvulsants
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Anti-gout drugs
SJS may also occur as a complication of certain medical conditions like:
- HIV
- Herpes
- Hepatitis
- Typhoid
- Influenza
- Diphtheria
Furthermore, radiation therapy is also known to trigger Stevens Johnson Syndrome.
Complications that may arise from Stevens Johnson Syndrome
SJS is a potentially deadly skin disease which requires immediate medical attention. Delaying the treatment may lead to life-threatening complications like:
- Cellulitis
This is an acute secondary infection of the skin which may result into meningitis.
- Eye problems
SJS can cause eye problems ranging from mild to severe. An individual may suffer from dry and irritated eyes if mild SJS occurs. Those with severe SJS may endure severe eye problems that could result to blindness.
- Permanent damage to the skin
SJS can cause lasting injury to the skin, such as abnormal pigmentation, bumps and scars.
- Sepsis
This is a life-threatening medical condition that could lead to organ failure caused by bacteria from severe infection.
- Organ damage
SJS can instigate lesions on the vital organs, resulting in the swelling of the kidneys, liver, heart and lungs.
Diagnosis of Stevens Johnson Syndrome
The diagnosis often involves considering the medical history of the patient as well as subjecting him or her to a physical examination. The doctor may also consider the distinctive SJS symptoms of the individual. He/she may request for skin biopsy by taking a tissue sample and subjecting it to careful analysis under the microscope.
Stevens Johnson Syndrome treatment
SJS usually requires hospitalization, some even necessitating burn centers or intensive care units. The treatment is often aimed at managing the symptoms experienced by the patient, which may involve:
- Discontinuation of the medication that caused SJS
The doctor may require the patient to discontinue all unnecessary medications in order to determine the drug that is causing the problem.
- Administering medications to relieve the symptoms
The patient may be given drugs, such as antihistamines, pain relievers, antibiotics and topical steroids to ease the symptoms. He or she may also be given intravenous immunoglobulin or corticosteroids to treat SJS.
- Supportive care
Supportive care may come in the form of eye care to prevent eye damage; wound care to facilitate the healing of wounds; fluid replacement to substitute fluid loss due to the shedding of skin. The patient must be well-nourished, and this could be ascertained by means of a nasogastric tube.
- Skin grafting
This is performed when a large part of the body has been affected by the disease. Skin grafting is done by harvesting skin from an unaffected part of the body and putting in the area that needs it. The procedure might also use synthetic skin replacement.
Stevens Johnson syndrome is a dreadful, potentially life-threatening disease that requires immediate medical attention. Various treatment options are available and recovery time differs between individuals, depending on the severity of the disease.
Stevens Johnson syndrome pictures