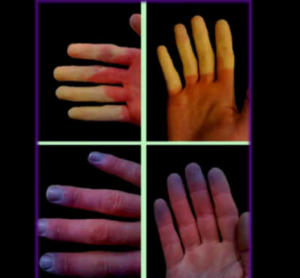
What is Raynaud’s Syndrome ?
Raynaud’s Syndrome or RS occurs due to the excessive constriction of blood vessels in the toes and fingers. People suffering from the syndrome find that the skin on their toes and fingers turn pale, or sometimes red or purple, when facing emotionally stressful situations or during cold weather. There are even times that the sufferers feel some pain on the affected areas.
Raynaud’s Syndrome is often associated with other medical conditions. It is for this reason that sufferers should seek medical treatment to resolve the underlying medical condition and prevent it from getting worse. If left untreated, the syndrome may result into graver health problems and even amputation.
Raynaud’s Syndrome and Disease – The Difference
The body’s normal reaction to emotional stress or extreme cold is to constrict the flow of blood to the surface of the skin to reduce the loss of heat and maintain the core temperature of the body. With Raynaud’s syndrome, the body overreacts to extreme cold by causing spasmodic contractions to the tiny blood vessels connected to the toes, fingers, face and ears. Due to these contractions, blood flow to these parts is reduced which results in color changes of the skin in these areas and manifestations of other symptoms.
The syndrome was named after Maurice Raynaud, a French physician who first described the condition in 1862. The term Raynaud’s Syndrome has been used in describing Raynaud disease. Though these conditions share the same name, they are different from each other nonetheless.
-
Raynaud Disease
This is referred to as primary Raynaud which is not related to any underlying medical condition. Experts believe that this form of Raynaud occurs due to a localized arterial defect and does not cause any serious consequence.
-
Raynaud Syndrome
This is referred to as secondary Raynaud which occurs with another medical condition. Secondary Raynaud may also be caused by the long-term use of vibrating tools or medications like chemo drugs, medications for migraine headaches and beta blockers. This form of Raynaud may progress to more serious health problems.
Causes of Raynaud’s Syndrome
Experts are still studying the exact cause of the syndrome and they believe that there are contributing factors that trigger its occurrence. Among these are:
- Connective tissue disorder
Connective tissue disorder, which is present in majority of the cases of Raynaud’s Syndrome, is a contributing factor in making the syndrome more serious. These disorders include MCTD (mixed connective tissue disease), systemic sclerosis (scleroderma), rheumatoid arthritis, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, Sjogren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Eating and obstructive disorders
Anoxeria nervosa, atherosclerosis and Buerger’s disease have been associated with Raynaud’s Syndrome.
- Certain medications
Beta blockers, chemo drugs and ergotamine drugs have been known to trigger the syndrome.
- Hand-arm vibration syndrome
People working in the drilling industry and working with vibrating tools have been observed to suffer from the syndrome too.
Raynaud’s Syndrome statistics
The syndrome had been found to occur more frequently in women than in men, specifically those who are in their 20s and 40s. Studies showed that it affects around 5% to 10% of the overall population of the United States. Also, people living in cold weather are more prone to developing the syndrome. Around 85% to 95% of those affected also have scleroderma and one-third of the sufferers have lupus.
The chances of developing Raynaud Syndrome are high among those who have the risk factors of the syndrome. Aside from being a female aged 20 to 40 years old, certain medications, diseases, injuries and activities may also put one at risk of developing the syndrome. Examples of these are typing, working on vibrating tools, playing the piano and exposure to some chemicals.
Raynaud‘s Syndrome symptoms
The most evident manifestation of the syndrome is skin discoloration. The phases of skin discoloration differ with each individual. White color occurs as a result of spasm which constricts the tiny arteries. The blue color appears when there are insufficient amounts of oxygen-rich blood. Numbness and coldness are also felt. Reddish color appears when the blood returns and the toes and fingers feel itchy and painful.
The prognosis differs with every patient, depending on what caused the syndrome and how severe it is. Raynaud Syndrome may lead to more serious conditions like skin ulcers and gangrene.
Diagnosis of Raynaud’s Syndrome
The diagnosis for Raynaud Syndrome involves lab panel tests to discount any underlying condition and autoimmune disorder that can cause the symptoms. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and anti-nuclear antibody test are often done to rule out autoimmune disorders.
Raynaud’s Syndrome Treatment
Treatment for Raynaud’s syndrome is targeted towards treating the underlying condition. This may involve using prescription medications, therapies and even surgery. Nothing could be done to prevent the disorder but precautionary measures prove beneficial in managing the effects of the syndrome and reduce the chances of complications. These often involve avoiding cold temperatures and staying warm; avoiding caffeine, quitting smoking and practicing proper stress management. Regular exercise also helps in promoting optimum blood flow.
While Raynaud’s syndrome has a treatment methodology which involves treating the underlying causes, the treatment options are the same for Raynaud’s disease.
Doctors prescribe like diltiazem or calcium channel blockers (nifedipine) but they may have side effects like flushing, headache but they are not severe and will not cause any complication as such. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists can reduce the intensity fo the attacks while Alpha-1 adrenergic blockers like prazosin can also be administered under the care of a good physician. Calcium channel blockers are also given as treatment for Raynaud’s syndrome. A topical cream known as RayVa is also prescribed as it contains an active ingredient called prostaglandin E1 and DDAIP to speed up the delivery of the medicine into the blood stream.
In more serious cases, the doctor may do a surgical procedure called sympathectomy, where the nerves that transmit that convey the messages of the fingertips are cut surgically. There is another form of surgery called microvascular surgery, which is surgery done with the help of the microscope. The latest development is the use of Botox for treatment.
To prevent Raynaud’s syndrome from aggravating, avoid environmental triggers like cold or vibration. Limit caffeine consumption, avoid smoking and keep extremities warm. During an emergency if you find the finger becoming white all of a sudden, run warm or tepid water on the affected fingers and massage the area gently. You should see the white area of the fingers turning to normal color. If there is no warm water available, place the digits in warmer place of the body like the mouth, the crotch or the under-arms. Keep the affected area in any of these places, till the blood circulation returns and the area gets back its healthy natural color.
Raynaud’s Syndrome pictures