What is Progeria?
What is Progeria?
Progeria is a genetic disorder that is progressive in nature and is characterized by rapid aging of children that usually begins in the first two years of their lives. Progeria is also known as Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome.
Children who are afflicted with progeria appear to be normal at birth. But after a period of about a year the signs and symptoms of progeria make an appearance in the form of hair loss and slow growth. Children who have being diagnosed with progeria tend to live an average life of about thirteen years. In some cases, children with the disorder may die at a younger age, while other may live as long as twenty years or more.
Motor as well as intellectual development in children with progeria stay normal, but the average height and weight generally tend to be lower than the average of other children of similar age.
Most of the deaths in children with progeria are caused due to strokes or cardiac problems. There is no known cure for progeria.
Symptoms of progeria
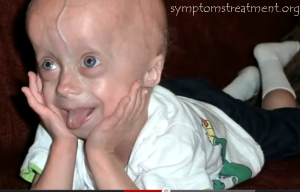
Some of the signs and symptoms of progeria are listed below:
- Growth and development that is slowed with height and weight that is below average
- A face that is narrowed along with a beak-like nose
- Loss of hair from the scalp as well as the eyebrows and the eyelashes
- The skin tends to tighten and harden on the trunk as well as the extremities of the body
- The head tends to be disproportionately large for the face
- Presence of thin lips
- The veins are easily visible through the skin
- The eyes are distinct and prominent
- The lower jaw is smaller than average and when compared to the rest of the face
- The voice has a high-pitched quality
- Tooth formation is abnormal and usually delayed
- The percentage of body muscle and fat is decreased or diminished
- The joints tend to be increasingly stiff
- There may be dislocation of the hip
- The body tends to be resistant to insulin
- Abnormalities and irregularities of heartbeat
Some of the complications that result from progeria include the following:
- The arteries are the blood vessels that carry the oxygen rich blood and other nutrients from the heart to the rest of the body. Progeria causes the hardening of these arteries in children leading to the stiffening and thickening of the walls of the arteries. This results in severe obstruction of blood flow from the heart.
- Progeria also leads to atherosclerosis and related complications
- Problems or defects in the blood vessels to the heart result in cardiovascular problems, congestive heart failure and cardiac arrest
- Problems or defects in the blood vessels to the brain result in cerebrovascular problems such as strokes
- Progeria does not cause other health related conditions associated with aging such as Alzheimer’s disease or far-sightedness
Causes of progeria
- Research studies have found out that progeria is caused due to the mutation of a single gene which is known as lamin A or the LMNA. The lamin A gene is responsible for producing a protein that is essential for holding the nucleus or the center of a cell combined or together. Theorists believe that this deficit caused due to the genetic mutation makes the cells unstable, thereby leading to the symptomatic aging process that is associated with progeria.
- Progeria is not passed down in families. Theory states that the mutation of the gene is new and usually occurs at the time of conception when a single egg or sperm gets affected by mutation.
- However, other similar syndromes such as the Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch syndrome has a genetic basis and tends to run in families. Fetuses that are affected by the Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch syndrome tend to age in the womb itself and the signs and symptoms become apparent after birth. The syndrome usually starts in adolescence or early adulthood and result in rapid aging as well as a shortened life span.
Treatment of progeria
- There is no cure for progeria. The disease can be managed by regular and constant monitoring of the health as well as the cardiovascular systems of the affected children.
- The progression of the disease may be slowed down with certain treatment methods such as coronary artery bypass surgery or angioplasty or dilation of cardiac arteries.
- A daily and low dose of aspirin can help prevent instances of strokes or cardiac attacks.
- The condition of the affected child may dictate the other medications. Statins may be prescribed to lower the cholesterol levels, anticoagulants may be used to assist in the prevention of blood clots and the intake of growth hormone may assist in increasing the weight and height.
- Hip problems as well as stiffness of the joints can be alleviated with occupational and physical therapy thereby allowing the child to stay active.
- Since rapid aging also brings early onset of adult teeth, the primary teeth or the baby teeth may need extraction.
- Research is continuing to find out ways and means to treat and cure progeria.
Progeria Pictures