When the immune system of the body responds in an adverse manner to a protein present in cow’s milk, then it produces allergic reactions in infants that can be life threatening. Such allergic are known as milk allergy in infants.
Milk allergy is different from milk intolerance. Infants may be allergic to then milk of goat, sheep, lamb, etc. as well and in some rare cases to soy milk. Most of the infants grow out of the allergies by the age of three to four years.
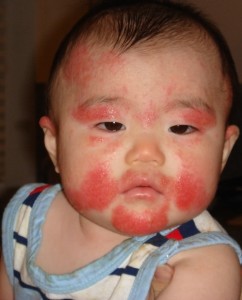
Symptoms of milk allergy in infants
The symptoms of milk allergy may vary from one infant to another. Some infants may show the symptoms within a few minutes after consuming milk formulas or cow’s milk, while others may take a few hours to show the signs of milk allergy.
Some of the symptoms and signs of milk allergy in infants are as follows:
- Wheezing
- Occurrence of hives in the body
- Vomiting
- Digestive issues like loose stools may occur sometime after the initial symptoms
- Increased flatulence
- Increased instances of gastric distress
- The fecal matter may have blood
- Cramps in the abdomen or stomach pain
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Increased migraines or headaches
- The wheezing may be accompanied by severe coughing
- The skin may develop rashes which are itchy and may be present mainly in the vicinity of the mouth
- Presence of a runny nose
- Itchy eyes or eyes that water
- Some newborns or babies may have colic
- In rare cases, milk allergy can lead to a life threatening condition like anaphylaxis.
- Anaphylaxis, may show signs such as flushing of the face, sever itching, narrowing of the airways which may result in problems in breathing, inflammation or swelling of the throat, a sense of shock and a noticeable drop in the blood pressure in infants
Causes of milk allergy in infants
Some of the causes and risk factors of milk allergy in infants are listed below:
- Almost all allergies are caused due to abnormalities of the immune system. Milk allergy in infants is also caused due to malfunction of the immune system. The immune system may mistake the proteins present in milk for harmful substance and produce antibodies, resulting in the increased manufacture of histamine and other chemicals to counter the invasion of the body. This triggers the allergic reactions in infants.
- The immune system is underdeveloped in babies and infants and hence there is a greater tendency for milk allergy in infants
- Infants who are allergic to other food products may be at greater risk for milk allergy
- Infants who have the atopic dermatitis condition are at increased risk to develop milk allergy
- A family history of food and other type of allergies increases the risk of the infants
Treatment of milk allergy in infants
- Avoidance of cow’s milk and milk of other animals as well as milk products is the best way to prevent milk allergy in infants.
- In case, there is milk allergic reaction in infants, then antihistamines and other such medications as advised by the doctor may help alleviate the signs and symptoms of distress and discomfort in infants
- If the milk allergic reaction causes anaphylaxis in the infants, then an epinephrine injection and a visit to a hospital is essential. Parents of infants, who are prone to the development of anaphylaxis as an allergic reaction to milk and milk products, must take extra precautions to avoid food items that contain milk as an ingredient, read the labels carefully and also carry shots or injections of epinephrine.
1historical