The Medulla Oblongata is a very important part of the brain as it supports a number of vital functions in the body. To mention a few, it is responsible for the involuntary movements such as the jerking of one’s hand, gag reflex and coughing. It is also responsible for the essential autonomic functions like the beating of the heart and the regulation of the lungs in breathing.
The Medulla oblongata is found at the tip of the spinal column at the base of the brain itself. This is also where the signals from different parts of the body pass through. This part of the brain is also responsible for the alertness of the human being; which is why anesthesia generally works to depress the activities of the medulla oblongata.
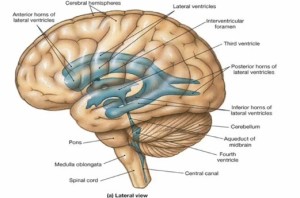
Medulla Oblongata location, anatomy
Found just right after the spinal column, the Medulla oblongata looks like a swell on top of the spinal cord. Its lower part is attached to the spinal cord through the central canal where the ventricles are found. The upper portion, meanwhile, is in line with the occipital bone of the head; whereas the lower anterior part of it is affixed to the cerebellum.
The following lists the parts that comprise the medulla oblongata:
- Median fissures – The median fissures closely appear like wrinkles. But these are actually small grooves or clefts that are found on the anterior part of the medulla oblongata. The anterior median fissures are interrupted by some bundles of nerves in the middle. After the nerves, on the lower part of the medulla oblongata, would be the posterior median fissures.
- Nerve rootlets – As aforementioned, the medulla oblongata is filled with nerves, which are generally called the surface characters. The medulla oblongata is divided into 2 regions, namely, the anterior and the posterior. On the anterior region, the nerve rootlets of hypoglossal nerves are found just in line with the spinal nerves. While on the posterior region, the glossopharyngeal nerves, the vagus nerves and the accessory nerves are found.
- Pyramid – The pyramid is found just beside the anterior median fissure. This would comprise of some of vital fibers that connect the medulla oblongata to the other parts of the brain in order to relay messages and signals. These important fibers include the corticospinal fibers which attach the medulla oblongata with the cerebral cortex and the pons; and the aborise fibers that connect the medulla oblongata to the anterior part of the spinal cord.
- Olive – The olive is found at the top most part of the medulla oblongata. The swelling of the olive is due to the nerves found inside it. The size of the olive is about 1.25cm long or about half an inch.
- Auditory nerves – The auditory nerves are the ones responsible for the interpretation of the sound waves that enter the brain. This is a part of the medulla oblongata and consists of 2 nerves, which are the cochlear nerves and the vestibular nerves. These are bundled together and separate when the nerves reach the lower border of the pons.
- Fasciculus gracilis – Fasciculus gracilis pertain to the bundle of fibers located on the tip of the spinal column and are also responsible for the relaying of messages. The gracilis have sensory fibers that send signals to the medulla oblongata via the posterior white column.
- Nerves – There are 8 cranial nerves that are attached to the medulla oblongata. These nerves in the medulla oblongata are connected to other parts of the brain. For instance, the fifth cranial nerve is connected to the brainstem. It has 1 nucleus in the middle of the brain and plenty more in the pons. The 6th nerve, meanwhile, is connected to the pons. The 7th and 8th nerves are attached to the pons. The 7th cranial nerve, however, is also attached to the upper part of the medulla oblongata. The 9th, 10th, and 12th cranial nerves are situated in the medulla oblongata entirely, while the 11th cranial nerve is found in the medulla oblongata and on the upper part of it as well.
Medulla oblongata damage and possible complications therein
If there is any injury incurred by the medulla oblongata, this could become fatal. It is known that the medulla oblongata holds plenty of vital functions such as the regulation of the heartbeat, the involuntary breathing and the pumping of the blood in the system. Without this part of the brain, or if it has sustained any form of damage, the person could die. For example, without any type of mechanical life support such as the ventilator that could help the person breath even if the lungs aren’t functioning normally, the patient would clearly expire.
Indeed, the Medulla Oblongata is one of the most important parts of our brain. It is crucial for blood pressure, breathing and other autonomic functions of the body, without which, the body person would be considered vegetative.