What is ingrown hair ?
Ingrown hair is a harmless skin disorder, most common among the youngsters and adults of darker skin. It usually occurs on shaved areas like face and neck.
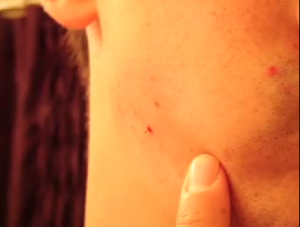
Ingrown hairs occur when the pointed tip of the hair turns back into the skin. They normally have the appearance of scattered red bumps and can be cosmetically disfiguring. Pink little bumps can be seen around hair follicles on the skin area that undergo frequent shaving. Skin infections which may occur get resolved by itself. Applying topical creams may help to control the ingrown hair.
Ingrown hair occurs after puberty and it is a very common skin disorder that tend to affect the regions of thicker and coarse hairs. Ingrown hair is clinically harmless, but cosmetically disfiguring and scarring.
Symptoms of Ingrown hair
- Tenderness and increased itching of the area with ingrown hair
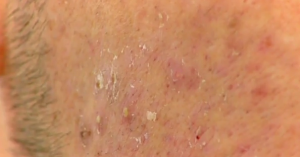
- Inflammatory reaction due to a localized foreign object in that area of Ingrown hair may cause pink bumps on skin. Also, the ingrown hair may occasionally be just visible at the center of the lump; at times the dry or pus-filled bumps remain scattered over the shaved area. The bumps may come up after few days from the time of hair removal. Acne white heads, which are called milia, can also be present in the region of ingrown hair.
- People with Ingrown hair may experience painful acne-like eruptions after shaving
- Pustules and rare abscesses can also appear due to infection by common bacteria, such as Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus, over the Ingrown hair area.
- Pseudofolliculitis known as ‘razor bumps’ is one type of ingrown hair, wherein five to forty small red bumps appear over the shaving area of lower face and the neck. The bumps with the hair shaft in center are seen, close to the hair follicle opening on the shaved area. Bacteria on skin form the pustules and abscesses. In untreated or chronic cases, scarring, post-inflammatory hyper-pigmentation and rare keloid disorder may also occur. This condition is seen in people with darker skin, due the curved nature of their hair.
Causes of Ingrown hair
- The hairs create a sharp tip, when they are cut short which can easily pierce through the skin and tend to cause the ingrown hair.
- The prime cause of ingrown hair is thought to be the adoption of improper shaving methods.
- Tight clothing which generates friction and waxing method of hair removal can worsen the condition.
- Apart from the aggressive and improper methods adopted in the hair removal, the other natural cause can be the presence of too much dead skin debris that blocks the opening of hair follicles, causing the hair growth sideways.
- Though almost all teenagers and adults get this Ingrown hair, it is more popular with those who have thicker and coarser hairs
Ingrown hair treatment
There is no cure available for ingrown hair. However maintaining hygienic skin and hair is the easiest way out.
- Hydrating and softening the skin and hair before shaving decreases ingrown hairs, as it may give rounded tip to the hairs and thus preventing its chances to reenter the skin.
- Salt or sugar that are the natural mild exfoliators may be applied to reduce the redness or irritation caused by the ingrown hairs.
- Use a wet cloth, mild soap, soft bristled brush, moistened sponge and wash the hair in circular motion for several minutes to make them soft and to dislodge the stubborn tips.
- Don’t shave against the direction of the hair growth and avoid close shaving.
- Allow the hair to grow as a natural solution.
- While using the electric shaver, let it be slow and circular in motion.
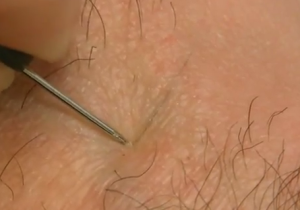
Avoid pulling the skin while shaving as it will result in a closer shave and allow the hairs to reenter the skin. - Using a sterile needle along with an alcohol wipe or tweezers to dislodge the ingrown hair is not advisable as it can damage the skin.
The ingrown hair heals on its own. However the available treatments are:
- Topical antibiotics
- Topical creams
- Chemical depilatories
- Removal of ingrown hair by small incision and pulling out the hair.
- Using hair removal laser.
Best results are achieved by combining the therapies. In severe cases, taking treatment from a specialist in dermatology may give better results.
- Using chemical depilatories every alternative day can loosen the hair and help in blunting the tips of shaved hair. Applying hydrocortisone can remove the irritation caused by the depilators.
- Topical corticosteroid cream application can reduce the inflammation of ingrown hairs.
- Topical tretinoin may help to thin out the epidermis and decrease the skin plugging, reduce the buildup of dead skins, and the ingrown hair.
- Topical antibiotics such as erithromycine and clindamycine for pustules and abscesses, and topical antibacterial agents such as Benzoyl peroxide for infection and their application in combination can help to reduce skin bacteria and treat secondary infections.
- Once or twice a day, antibacterial lotion wash with benzoyl peroxide or chlorhexide can control infection.
- Oral antibiotics such as tetracycline orcephalexin can treat infected pustules and abscesses.
- Applying topical eflornithine HCL 13.9% cream can reduce hair growth as a long term relief.
- Generally laser hair removal is faster, efficient and safe to decrease permanently the number of hairs. Skin discoloration is the risk involved.
- Creams such as hydroquinone 4%, kojic acid, azelaic acid 15%-20% can improve skin discoloration.
- Electrolysis can be used to remove the hair permanently and destroy hair follicles. But it is slow and tedious, requiring multiple treatments.
Ingrown hair pictures