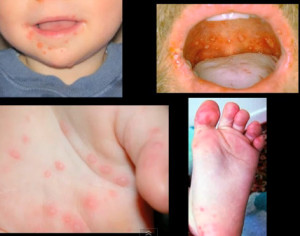
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a contagious and mild viral infection that is commonly found in young children. It leads to the development of a rash on the feet and hands as well as sores in the mouth. The most common cause of hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a coxsackievirus.
There are no special methods to treat hand-foot-and-mouth disease. One can prevent instances of the condition and reduce the risk to the disease by maintaining good personal hygiene that involves through washing of the hands, feet and other body parts.
Hand foot and mouth disease symptoms
There are several signs and symptoms of hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Some individuals may show all the signs, whereas some may show only a few of the symptoms mentioned below:
- Fever
- A general feeling of malaise or being unwell
- Increased soreness of the throat
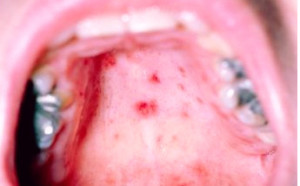
- The gums, tongue and the inside part of the cheeks may develop red, painful and blister like lesions
- Toddlers and infants may experience increased irritability
- A red rash, without itching but sometimes with blistering, on the palms, soles and sometimes the buttocks
- A non-itchy, red rash that occasionally causes blistering may appear on the soles and palms and sometimes on the buttocks
- Poor appetite
The incubation period or the period from initial contact with infective germs to the development of symptoms lasts for 3 days to a week. The first symptom of hand-foot-and-mouth disease is fever that is followed by sore throat and occasionally by malaise and loss of appetite. A day or two after the onset of fever, the mouth or throat may develop sores that are very painful. This may eventually be followed by a rash on the feet and hands and sometimes on the buttons.
- Dehydration is the most common complication caused due to hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Infants and children find it very difficult and painful to swallow food and other liquids due to the mouth sores. Hence it is important that parents take active measures to prevent any dehydration in their children affected by hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
- There are some other serious complications such as encephalitis and viral meningitis that may be caused due to the infection of the brain and its tissues by the virus. In such cases, one must immediately consult a doctor.
Hand foot and mouth disease causes
Infection and contact with the coxsackievirus A16 is the most common cause of hand-foot-and-mouth disease. This virus comes from family of viruses known as nonpolio enteroviruses. Occasionally, other forms of nonpolio enteroviruses may also cause hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
Individuals generally tend to get infected by the coxsackievirus through oral means. The disease is contagious and hence can spread from one person to another via contact with an infected individual. The spread of hand-foot-and-mouth disease can take place through:
- The respiratory droplets that are released into the air via a sneeze or cough
- Throat discharge or nasal secretions
- Contact with blister fluids
- Contact with saliva
- Contact with stool
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is most likely to be found and spread in child care settings. This is due to potty training and frequent diaper changes. Also, it is more likely that toddlers and infants will put their hands in their mouths.
It is important to note that even though infected infants are most contagious during the first few weeks of hand-foot-and-mouth disease, they still tend to carry the virus long after the signs of the illness have subsided. Hence they can still infect others with the virus. Some individuals, mostly adults can pass on the condition without showing any signs or symptoms.
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is most common during autumn and summer months in the United States. In tropical climates, the illness is prevalent throughout the year.
The disease is different from foot and mouth disease that affects the farm animals. Humans cannot contact hand-foot-and-mouth disease from pets or other animals, nor can they infect the animals with the condition.
As children grow older, the immune system of the body develops antibodies to the virus and they tend to become immune to hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
Hand foot and mouth disease treatment
- There are no specific treatment methods for hand-foot-and-mouth disease. The disease runs its course and the symptoms tend to disappear on their own within seven to ten days.
- One may use a topical oral anesthetic to alleviate the pain caused by the mouth sores. Once can also take over the counter medications such as ibuprofen to reduce the discomfort. It is essential to note that children should avoid the intake of aspirin.
Some types of beverages and food items tend to irritate the sores in the mouth and make for difficult ingestion of food. One can try these tips to relieve the general discomfort and make the blisters less irritable so that food consumption is easier:
- Sucking on ice chips or ice pops
- Consume cold beverages like ice water and cold milk
- Drink sherbet or eat ice cream
- Acidic beverages and foods such as fruit drinks, soda and citrus fruit should be avoided
- Consume soft foods that do not require a lot of chewing
- Salty and spicy foods should be avoided
- Rinse the mouth with warm water after consuming food
- In case the infant is able to rinse the mouth without swallowing, then one can resort to rinsing the mouth with warm water mixed with salt, several times a day, to alleviate the inflammation and pain caused in the mouth due to hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
Hand foot and mouth disease pictures
Check out the photos of hand, foot and mouth disease and see how these specific parts in the body are affected.