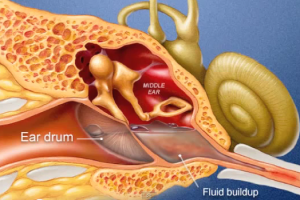
An ear infection or acute otitis media refers to a viral or bacterial infection of the middle ear, which is a space posterior to the eardrum that is filled with air and encloses the small, vibrating bones of the ear. Children are at greater risk to ear infection than adults.
Ear infection causes accumulation of liquids in the middle ear as well as inflammation that result in pain.
Most cases of ear infection resolve on their own and hence treatment if aimed at monitoring the issue and controlling pain. Ear infection that affects infants and those cases which are severe are treated with antibiotics. Chronic problems associated with ear infections such as continuous infections and presence of fluids in the ear, can lead to hearing difficulties and other extreme complications.
Ear infection symptoms in children
These include :
- Pain in the ear, particularly while lying down
- Sleeping problems
- Pulling or constantly clutching the ear
- Increased instances of crying
- Problems in hearing sounds or responding to them
- Increased irritability
- Diminished sense of balance
- Fever with temperature of 100 degree Fahrenheit or more
- Headaches
- Leakage of fluid matter from the ear
- Vomiting
- Appetite loss or lack of it
- Diarrhea
Ear infection symptoms In Adults:
There are actually two types of ear infections that can affect adults, outer ear infections and acute middle ear infections. Commonly, what adults get are outer ear infections or otitis externa while in some cases, adults can also get otitis mediaor middle ear infections.
Ear infection symptoms in adults – Outer Ear (Swimmer’s ear)
This is also called ‘swimmer’s ear’ because it is seen mostly in swimmers. It happens when contaminated water accumulates in the outer ear, becoming a hot-bed for germs and microbes to thrive under moist, warm conditions. The symptoms for outer ear infections in adults include –
- Redness in the ear
- Itchy feeling inside the ear
- Pain
- Fever
- Pain when you touch your ear, or even when you move your head
- Flaking on the skin of the ear
The doctor can easily diagnose Swimmer’s ear and the condition can be treated with antibiotic ear drops.
Ear infection symptoms in adults – Middle Ear (Otitis Media)
Though this is more common in children, this type of ear infection can affect adults too. This happens when adjoining tissues in the nasal area and the throat can block the Eustachian tube (tiny tube that begins in the ear and goes into the back of the throat) and does not permit draining. So, if you are suffering from cold, get seasonal allergies or are flying on an airplane, you can get this type of middle ear infection. It is also caused due to insertion of foreign objects like Q-tips in the ear.
The symptoms are –
- Pain in the ear
- Fever
- Leakage from air, happens possible due to ruptured ear drum
- Vertigo
- Feeling that there is pressure building in the air
- Hearing loss
One must get the middle ear infection treated by an ENT specialist.
Ear infection complications
Some of the complications that may result from ear infection include:
- Compromised hearing: Most cases of ear infection tend to result in some form of temporary hearing loss. Once ear infection is cleared, hearing returns to normal. However, chronic and prolonged cases of ear infection can lead to significant loss of hearing. Any permanent damage to the middle ear structures or the eardrum due to ear infection can result in permanent loss of hearing
- Infection spread: Infections that do not resolve fully or untreated ear infection cases can lead to its spread to the adjacent tissues. Infection of the bony structure behind the ear is known as mastoiditis and lead to development of pus cysts and bone damage. In rare cases, the infection may spread to the brain
- Developmental and speech delays: Temporary or permanent loss of hearing in toddlers and infants can lead to delays in the development of speech, language and social skills.
Causes of Ear infection
Ear infection is caused due to infection of the middle ear by bacteria or virus. Such infection may be caused due to the presence of other infections such as flu, cold or allergy, that results in clogging of the throat, nasal passageway and Eustachian tubes.
Eustachian tubes: They are a pair of thin tubes that go from the middle ear to the back of throat, behind the nasal passageways. The ends of the tubes near the throat close and open to control the middle ear air pressure, remove middle ear normal discharges and to refresh the air present in the ear. An allergy or upper respiratory infection can cause inflammation, mucous and swelling of the Eustachian tubes. Such fluids can get blocked and deposit in the middle ear. Viral or bacterial infections of these fluids lead to ear infection. The tubes are more horizontal and narrower in children, which prevents easy drainage of middle ear fluids. Hence children are at greater risk for ear infection
Adenoids: They are tiny pads located at the back of the throat and hence any swelling, inflammation or infection of adenoids can result in blockage of the Eustachian tubes. This causes ear infection. Children have larger and more active adenoids and hence they are more vulnerable to ear infection
Some factors that increase the risk to ear infection are as follows:
- Children between the ages of six months and two years
- Children who are bottle fed while lying down are at greater risk to ear infection
- Children in day care centers are more likely to contract cold, flu and other infections, increasing the risk to ear infections
- Increased exposure to polluted air or tobacco smoke
- Seasons such as winter and fall increase the risk to cold, flu, etc. and hence to ear infection
- Inuits of Canada and Alaska as well as American Indians are at greater risk to ear infection than others
- A family history of ear infections
Ear infection treatment
- Most cases of ear infection fade away and resolve without any treatment. However, if ear infection symptoms do not improve in a couple of days, then consult a doctor. If the problem persists taking into consideration, the ear infection symptoms mentioned above, get in touch with a doctor or even better, an ENT specialist
- Ear drops, pain medications and warm compresses may be advised for alleviating the ear pain
- Antibiotics may be prescribed by a doctor to treat ear infection, if deemed necessary
- In case, there is presence of fluids in the ear even after ear infection resolution, then the doctor may recommend manual drainage of the liquids from the ear
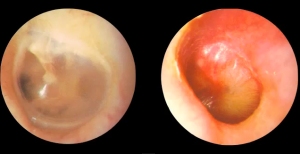
Ear Infection pictures
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thanks , I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
Woah! I’m really loving the template/theme of this website. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s very hard to get that “perfect balance” between user friendliness and appearance. I must say you have done a fantastic job with this. Also, the blog loads very quick for me on Chrome. Excellent Blog!