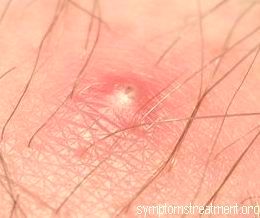
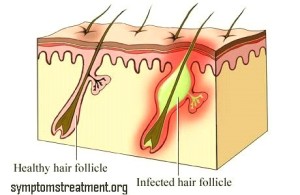
Infected ingrown hair or ingrown hair is a benign condition wherein the end or the tip of hair grows back into the skin. This condition is more prevalent in individuals who have thicker and coarser hair such as African-Americans.
Infected ingrown hair may cause swelling and inflammation of the skin which results in pain and discomfort.
Symptoms of infected ingrown hair
• Infected ingrown hair often happens after puberty and occurs in areas where the hair may be shaved, tweezed or plucked. In men, ingrown hair may occur in the cheeks, the chin and more often in the neck. Men who shave their heads may have instances of infected ingrown hair on the head. In women, ingrown hair occurs in the pubic area, the legs and the armpits.
Some of the symptoms of infected ingrown hair are as follows:
• There is hyper pigmentation or darkening of the skin
• There are small, hard bumps which are round in shape, in the areas where there is a case of infected ingrown hair.
• The bumps are may be red or pink in color indicating inflammation or infection of the area
• Embedded hair may be accompanied by severe itching and pain
• Small lesions or pustules which are filled with pus and look like blisters.
• Tenderness of the area affected by infected ingrown hair
• Increased instances of acne
• The skin on the area that has been shaved and infected with ingrown hair may have a flushed red appearance due the dilation of the blood vessels on the surface of the skin.
Causes of infected ingrown hair
Some of the causes of infected ingrown hair are listed below:
• Improper ways and techniques of shaving may result in the development of infected ingrown hair. When the hair is shaved very close to the skin it leaves a sharp tip at the end of the hair. This increases the likelihood of the hair to grow inwards or sideways
• Waxing, tweezing or other aggressive methods to remove hair result in ingrown hair
• Curly hair has a greater tendency to grow inward than normal straight hair.
• The presence of extra dead skin on the surface may prevent the hair from growing out and result in an infected ingrown hair
• Infection or inflammation of the skin is a natural and adverse reaction of the skin to an ingrown hair.
Treatment of infected ingrown hair
Some of the treatment and preventive methods of infected ingrown hair are as follows:
• Topical steroid medications or ointments like corticosteroids to help alleviate inflammation and swelling.
• Stop following incorrect and aggressive methods or techniques of hair removal
• Creams such as retinoids may be applied on the skin to clear the dead skin and skin cells. It may also help in decreasing the pigmentation of the skin
• Topical antibiotics to prevent infections that may result from frequent scratching of the affected and itchy area. The physical may also prescribe oral antibiotics.
• In case, one needs to shave an area affected with infected ingrown hair, one should wash that area with a soft cloth in circular movements for a few minutes before proceeding to shave.
• Other preventive methods include proper techniques of shaving like wetting the hair with warm water prior to a shave, use of a single blade and sharp razor, use of a good lubrication foam or gel, avoiding close shaves, rinsing the blade after each shave and applying cool after-shave lotion after the process of shaving hair is over.
Infected ingrown hair pictures
rialto apartments the loop apartments chapel hill apartments